|
|
POLYDIMETHYLSILOXANE Prepared at the 37th JECFA (1990), published in FNP 52 (1992) superseding specifications prepared at the 29th JECFA (1985), published in FNP 34 (1986). Metals and arsenic specifications revised at the 61st JECFA (2003). An ADI of 0-1.5 mg/kg bw was established at the 23rd JECFA (1979) | |
|
SYNONYMS |
Poly(dimethylsiloxane), dimethylpolysiloxane, dimethylsilicone fluid, dimethylsilicone oil; INS No. 900 |
|
DEFINITION |
Consists of fully methylated linear siloxane polymers containing repeating units of the formula (CH3)2SiO, with trimethylsiloxy end-blocking units of the formula (CH3)3SiO- The article of commerce used as an antifoaming agent can be further specified as to total silicon |
|
Chemical names |
Simethicone (CAS name) |
|
C.A.S. number |
8050-81-5 |
|
Formula weight |
6,800 to 30,000 (average and approximate) |
|
Assay |
Silicon content not less than 37.3% and not more than 38.5% of the total |
|
DEION |
Clear, colourless, viscous liquid. Polydimethylsiloxane is frequently used in commerce as such, as a liquid containing 4-5% silica gel, and as an aqueous emulsion formulation containing, in addition to silica gel, emulsifiers and preservatives. The pure substance described here can be isolated by centrifuging from the silica gel-containing liquid at about 20,000 rpm. |
|
FUNCTIONAL USES |
Antifoaming agent, anticaking agent |
|
CHARACTERISTICS | |
|
IDENTIFICATION | |
|
Solubility (Vol. 4) |
Insoluble in water and in ethanol; soluble in carbon tetrachloride, benzene, chloroform, diethyl ether, toluene and other organic solvents |
|
Specific gravity (Vol. 4) |
d (25, 25): 0.964 - 0.977 |
|
Refractive index (Vol. 4) |
n (25, D): 1.400 - 1.405 |
|
Infrared absorption |
The infrared spectrum of the sample corresponds with the reference infrared spectrum below. Prepare two solutions containing: (1) 10% of sample in carbon tetrachloride and (2) 2% of sample in carbon disulfide. Obtain the infrared spectrum for the sample using the carbon disulfide solution (2) from 1300 to 650 cm-1. The solvent in the reference cell is also changed at the appropriate wave numbers to correspond to the sample solution. |
|
PURITY | |
|
Loss on drying (Vol. 4) |
Not more than 0.5% (150o, 4 h) |
|
Viscosity |
100 - 1500 cSt at 25o See deion under TESTS |
|
Lead (Vol. 4) |
Not more than 1 mg/kg Determine using an atomic absorption technique appropriate to the specified level. The selection of sample size and method of sample preparation may be based on the principles of the method described in Volume 4, "Instrumental Methods." |
|
TESTS | |
|
PURITY TESTS | |
|
Viscosity |
Apparatus: The Ubbelohde suspended level viscometer, shown in the accompanying diagram, is preferred for the determination of the viscosity. |
ادامه مطلب... تاریخ : شنبه 87/12/24 | 7:26 عصر | نویسنده : مهندس سجاد شفیعی | نظرات () | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Danish Name |
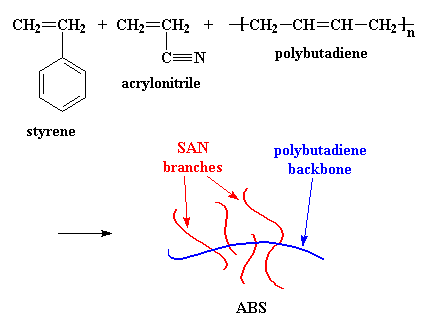
ABS - acrylnitril-butadien-styren-terpolymer |
Category |
Plastics, Thermoplastics |
Products |
LEGO building bricks Computer mouse Vacuum jug KimBox suitcase Ceramic advanced wet shave razor Hedge cutter handle Handle for high pressure cleaner Shaver, rechargeable Ensemble chair (ABS blended with PA) |
Processes |
Plastic moulding Plastic injection moulding Extrusion Vacuum forming Printing |
Similar materials |
SAN ASA SB |
Price |
Medium cost plastic (see also Plastics general overview) |
Environmen- tal notes |
Creation: Production of 1 kg of ABS requires the equivalent of about 2 kg of oil (raw material and energy). Use: - Disposal: Incineration in an incineration plant mainly produces water, carbon dioxide and nitrogen compounds. |
Additional Info |
ABS is resistant to some bases but not to other solvents than alcohol. Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer Properties:
ABS is derived from acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene. Acrylonitrile is a synthetic monomer produced from propylene and ammonia; butadiene is a petroleum hydrocarbon obtained from the C4 fraction of steam cracking; styrene monomer is made by dehydrogenation of ethyl benzene - a hydrocarbon obtained in the reaction of ethylene and benzene. The advantage of ABS is that this material combines the strength and rigidity of the acrylonitrile and styrene polymers with the toughness of the polybutadiene rubber. The most important mechanical properties of ABS are resistance and toughness. A variety of modifications can be made to improve impact resistance, toughness, and heat resistance. The impact resistance can be amplified by increasing the proportions of polybutadiene in relation to styrene and also acrylonitrile although this causes changes in other properties. Impact resistance does not fall off rapidly at lower temperatures. Stability under load is excellent with limited loads. Even though ABS plastics are used largely for mechanical purposes, they also have good electrical properties that are fairly constant over a wide range of frequencies. These properties are little affected by temperature and atmospheric humidity in the acceptable operating range of temperatures.[4] The final properties will be influenced to some extent by the conditions under which the material is processed to the final product; for example, molding at a high temperature improves the gloss and heat resistance of the product whereas the highest impact resistance and strength are obtained by molding at low temperature. ABS polymers are resistant to aqueous acids, alkalis, concentrated hydrochloric and phosphoric acids, alcohols and animal, vegetable and mineral oils, but they are swollen by glacial acetic acid, carbon tetrachloride and aromatic hydrocarbons and are attacked by concentrated sulfuric and nitric acids. They are soluble in esters, ketones and ethylene dichloride. The aging characteristics of the polymers are largely influenced by the polybutadiene content, and it is normal to include antioxidants in the composition. On the other hand, while the cost of producing ABS is roughly twice the cost of producing polystyrene, ABS is considered superior for its hardness, gloss, toughness, and electrical insulation properties. However, it will be degraded (dissolve) [5] when exposed to acetone. ABS is flammable when it is exposed to high temperatures, such as a wood fire. It will "boil", then burst spectacularly into intense, hot flames. |
References of this text are :
http://www.matweb.com/ & http://www.designinsite.dk/ & http://www.icis.com/ &
|
سلام دوستان عزیز - همانطوری که یکی از دوستانم خواسته بود راجع به تعداد زیادی از پلیمر های مشهور یک سری لینک کلی گذاشتم . هر چند که توضیح مفصلی راجع به خیلی از این پلیمر ها از سنتز گرفته تا کاربرد و غیره تو پست های قبلی وبلاگم هست ولی بنا به درخواستتون باز هم اینجا گذاشتم . حتی راجع به کلی از کوچک مولکولها هم میتونید مطلب پیدا کنید . | |
Reference of this text is : http://www.icis.com/
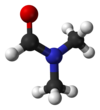
 see also information about DMF in Wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dimethylformamide ( لینک مربوط به دایره المعارف ویکیپدیا راجع به دی متیل فرماماید )
see also information about DMF in Wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dimethylformamide ( لینک مربوط به دایره المعارف ویکیپدیا راجع به دی متیل فرماماید )Polyglycine
DOUGLAS G. GOLD AND WILMER G. MILLER
TRADE NAME:
Nylon 2CLASS: Polypeptides and proteins
MAJOR APPLICATIONS:
Serves as a model for various proteins.PROPERTIES OF SPECIAL INTEREST:
Two crystalline forms of polyglycine, I and II, havebeen observed. Form I is thought to have a
structure where the individual chainsexist in a helical conformation and form sheets stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
The individual chains in form II also have a helical conformation but are packed in
a hexagonal lattice with a three-dimensional array of hydrogen bonds.
SYNTHESIS: The synthesis is similar to that of poly(-benzyl-L-glutamate). (See alsothe entry on
Poly(-benzyl-L-glutamate) in this handbook.) It involves the conversionof the amino acid to the N-carboxyanhydride (NCA) monomer by reaction with
phosgene gas followed by polymerization of the NCA with an appropriate initiator
(e.g., triethylamine). Typical comonomers include other amino acid NCAs.
reference of this text that you can find good informtion about Nylon 2 in it is :
Polymer Data Handbook
. Copyright # 1999 by Oxford University Press, Inc. All rights reserved.
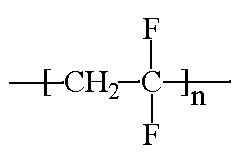
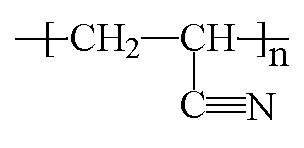
ACRONYMS, TRADE NAMES: PVDF, PVF2, Kynar, Solef, Neoflon, Foraflon, KF, Soltex
CLASS: Vinylidene polymers
Poly(vinylidene fluoride), or PVDF, has a few things going for it. It has very high electrical resistance, and it has good flame resistance. Put these two bits of information together and it might dawn on you that this would make a good material for insulating electrical wires, especially ones that get hot during use. So you"ll find it insulating the wires in the computer you"re using right now. Electrical cables on airplanes are also insulated with PVDF, where it"s important that practically everything on board be fireproof. It"s also chemically resistant, so you"ll find it used in the chemical industry to make pipes and bottles and such that hold chemicals. What about ultraviolet radiation? PVDF resists that, too. PVDF is often blended with poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) to make it more resistant to UV light. PMMA degrades when exposed to UV radiation, so if we want to make PMMA windows for use outside we have to blend it with PVDF.
Another nifty thing about PVDF is that it"s a piezoelectric material. What does that mean? That means that when it"s placed in an electric field it changes its shape.
Because fluorine is so much more electronegative than carbon, the fluorine atoms will pull electrons away from the carbon atoms to which they are attached. This means the -CF2- groups in the chain will be very polar, with a partial negative charge on the fluorine atoms and a partial positive charge on the carbon atoms. So when they"re placed in an electrical field, they align. This causes the polymer sample to deform, all those -CF2- groups trying to align.
Now here"s the fun part:
If you put it in an alternating electrical field it"ll vibrate, deforming in one direction, and then in the opposite direction. This vibration can be used to produce sound. This is how piezoelectric tweeters work.
PVDF is made by free radical vinyl polymerization of the monomer vinylidene fluoride, like this:
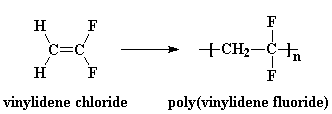
PropertiesGlass transition temperature: -38oC. Melting temperature: 160oC. Amorphous density at 25oC: 1.74 g/cm3. Crystalline density at 25oC: 2.00 g/cm3. Molecular weight of repeat unit: 64.03 g/mol.
MAJOR APPLICATIONS:Wire and cable insulation, tubing, piping, sheet and melt-cast®lms for electrical and electronics, binder for high-quality metal ®nishes for uilding components used on exterior wall panels, roo®ng shingles, and on industrial, commercial and residential buildings, used in fluid handling systems for solid and lined pipes, ®ttings, valves, and pumps, in manufacture of microporous and ultra®ltration membranes, chemical-tank lining, telephone headset, infrared sensing, hydrophones, keyboards and, printers. PROPERTIES OF SPECIAL INTEREST:Excellent mechanical properties and resistance to severe environmental stress, good chemical resistance, good piezoelectric and pyroelectric properties PREPARATIVE TECHNIQUES Emulsion polymerization: (a) 300±800 psig, perfluorinated surfactant initiator, 65±858C, 2±6 h; (b) 200 lb in2, 50±1108C, fluorinated surfactant, 17±21 h, iron powder. Suspension polymerization: suspending agent, reaction accelerator, water soluble initiator, 300±1,000 psig, 35±1008C.
click this for Typical physical properties references of this text are : 2- http://www.polymerprocessing.com/ 3- Polymer Data Handbook. Copyright # 1999 by Oxford University Press, Inc. All rights reserved. |
Polyethylenes: Polyethylene (PE) Low density polyethylene (LDPE) High density polyethylene (HDPE) Crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE)
Polypropylenes: Polypropylene (PP) Polybutylene (PB) Polyisobutene (PIB) Biaxially-oriented polypropylene
Polyarylates: Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) polymethyl acrylate (PMA) hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) polybutadiene acrylonitrile (PBAN) Sodium polyacrylate polyacrylamide (PAM)
Polyesteres: Polystyrene (PS) Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) High impact polystyrene (HIPS) Extruded polystyrene (XPS)
Polysulphones: Polysulfone (PSU) Polyarylsulfone (PAS) Polyethersulfone PES Polyphenylsulfone (PPS)
Polyamides: Polyamide (PA) polyphthalamide (PPA) Bismaleimide (BMI) urea formaldehyde (UF)
Polyurethanes: Polyurethane (PU) Polyisocyanurate (PIR)
Polyvinyls: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC)
Fluoropolymers: Fluoropolymer (FE) Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Ethylene chlorotrifluoroethlyene (ECTFE)
Polycarbonate (PC) Polylactic acid (PLA)
reference of this text is : http://plastics.inwiki.org/
New magnetic polymers may advance spintronics technologies

The magnetic polymer is produced when copper ions bind to pyrazine molecules creating a sheet-like structure, shown in the blue-purple crystals. Like a Tinkertoy ® building block, the bifluoride ion, shown in green, acts as a bridge to hold the planes together. The product is a three-dimensional coordination polymer, held together by one of the strongest hydrogen bonds known, making this a very thermally stable material. Credit: Argonne National Laboratory
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy"s Argonne National Laboratory have pioneered a new approach for making magnetic polymers that are held together with very strong hydrogen bonds. These polymers contain an innovative bifluoride, HF2–, building block that allows a magnetically ordered state to be obtained. The development may help lead to new techniques for faster and more versatile computer chips, among other applications.
reference of this text is : http://www.physorg.com/


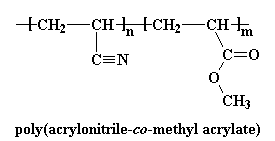
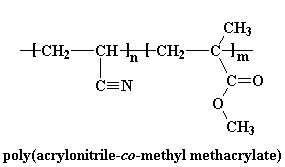
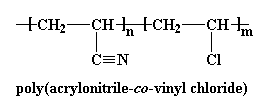
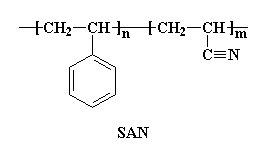
 ABS is very strong and lightweight. It is strong enough to be used to make automobile body parts, but it is so light that Wassana can lift this front bumper fascia over her head with only hand! Using plastics like ABS makes automobiles lighter, so they use less fuel, and therefore they pollute less.
ABS is very strong and lightweight. It is strong enough to be used to make automobile body parts, but it is so light that Wassana can lift this front bumper fascia over her head with only hand! Using plastics like ABS makes automobiles lighter, so they use less fuel, and therefore they pollute less.  ABS is a stronger plastic than
ABS is a stronger plastic than 



